- Home Page
- ECC Books
- ECC Reliability Database
- ECC Projects
- Consulting Services
- News 2025
- Products
- Contact
- Papers
- Partners
- ECC Academy 2025
- Career Coaching
- ECC Team
Scientific Papers
Vulnerability Analysis methodology: The vulnerability prediction based on the expected number of heavy storms and flood in Rio de Janeiro city.
Abstract: The society's vulnerability to natural disasters are increasing since the environment, climate changing in the last 10 years. Nevertheless, the vulnerability perception of the society, including the public and private sector leaders is still low which can be realized based on the last catastrophic natural disaster events around the globe. Therefore, the first step in a direction to increase the authorities and leader vulnerability perception is to assess the expected number of future natural disasters as well as its consequences. In order to provide a methodology to approach this problem the paper proposes the prediction of the expected number of natural disasters based on the Crow AMSSA model as well as the final prediction of the vulnerability based on Bow tie analysis. The vulnerability criteria are also proposed as a baseline to support leader to take decision regarding the necessity to reduce their vulnerability face of natural disasters.
Keywords: Vulnerability, expected number of storms, mean time between storms, Acceptable vulnerability, Bow Tie model.
The Human factors in the Hybrid Risk analysis approach: FTA, BTA and HRA integrated approach applied to assess the influence of human error to the risk of Plant shutdown.
Abstract:The paper aim to demonstrate the importance of human error in risk analysis by applying the hybrid risk analysis, which encompasses the Fault Tree Analysis as well as
the Bow Tie Analysis, including the human error probability as a result of human reliability analysis. Therefore, the brief explanation of the risk analysis such as FTA and BTA as well as
different human reliability analysis, such as ASEP, SPAH-R and HEART
will be presented. In order to exemplify the importance of hybrid risk analysis considering human factor, the emergency shutdown, valve (ESDV) procedure case will be demonstrated which consider
the real time in response event based on dynamic simulation results. The result will show how important is to consider human factors together with risk analysis to support decisions during an
operational critical event which can lead a total plant shut down.
Key words: Fault Tree Analysis, Bow Tie Analysis, Hybrid Analyis, Human reliability Analysis,ASE P, SPAH-R, HEART
Using network methodology to define emergency response team location: The Brazilian refinery case study
Abstract: The main objective of this study is to define Emergency Response Team Location in a specific area based on the risk of plants and facilities. The Center of Gravity and
Haikini Network methodologies are the two different approaches used to define the location in a network based on index values and distance between locations. These methodologies are different in
regard to one basic concept concerning the possibility of defining critical locations in the network in the first case and their boundaries in the second case. The index in this case will be the
frequency of hazardous events in each facility or plant located in the network. The two methodologies will be implemented and the results will be assessed. Therefore, a sensitivity analysis will
be carried out looking at specific elements such as alternative routes and population dislocation in the case of accidents. Furthermore, the real historical data and the usual data used in Brazil
in hazardous event will be assessed to check the influence on final results.
The refinery case study will be carried out to define the Emergency Response Team location in a Brazilian refinery.
key words: Center of Gravity method, Haikini Network methods, risk, Safety reliability, Safety availability, emergency team availability.
Environmental reliability as a requirement for defining environmental impact limits in critical areas
ABSTRACT: The main objective of this study is to define reliability requirements concerning environmental impacts caused by asset in critical areas in terms of environmental
resource sensitivity. Nowadays many risk criteria in Brazil are evaluating different oil and gas assets probable environment impact during environmental license process, but the
environmental impact of the group of oil and gas assets together or the impact of a new asset in an area with many asset is not been taking into account.
When the number of oil and gas asset in a specific area increases the risk of accidents is also increase. In other words , the reliability over time gets worse. Unfortunately, most of cases in
Brazil do not take into account the risk of environmental impact caused by the group of oil and gas asset in a specific area and the decreased of reliability over time.
The methodology proposed takes into account all the critical events which cause a serious environmental impact for each asset in the same area that may take place over time. By taking into
account all relevant events, it is possible to produce the Environment Diagram Block which covers all related events and their probability of occurring over time. That means , the failures in any
is represented in diagram reliability block which represents an accidents with potential environment impacts.
The environmental reliability target is associated with the tolerable number of environmental impacts in a specific area, taking into account all events over a specific period of time. The
tolerable number of accidents depends on social perception and environmental sensitivity.
For this analysis, the Monte Carlo simulation has to be carried out over a period of time in order to define the Environmental Availability and Environmental Reliability related to the number of
tolerable events. Moreover, in the case of any Asset modifications or an increase in the number of enterprises a new diagram block block will be inputted in the Environmental Block Diagram
and the new results will be assessed.
Keywords: Environmental Impact, Environmental Reliability, number of environment impact, environment impact, reliability block diagram.
The integrated Preliminary Hazard Analysis methodology regarding environment, safety and social issues: The platform risk analysis study case
ABSTRACT: The preliminary risk analysis is one of the most popular risk analysis tools in Brazil and it’s been used in so many Industries and enterprises, to support decision in
terms of risk mitigation. In most of cases, despite the application, it’s has been not regarding societal economic losses. During asset operation, The PHA has been done before a specific
operational activity but in case of project it’s necessary to have an integrated approach regarding environment, safety, health, organization image and impact of local society
economy.
The mean objective of this study is propose an Integrated Preliminary Risk analysis approach to support decision in risk mitigation and it’ll be applied to a Platform case study to demonstrate
the proposed methodology.
The study steps will be definition of risk qualification with it’s probability and consequence range, systems and subsystems definitions, hazards and environment aspect , recommendations to risk
mitigation, and finally,
the critical analysis about this methodology regarding positive and negative point.
Key Words: Risk Assessment, Risk Matrix, Severity category, frequency category, social economic impact valuation.


The safety integrity level as Hazop Risk Analysis consistence. The Brazilian risk analysis study case
Abstract:
The HAZOP is the most used risk analyze tool in Brazilian oil industry and it’s has been given
the high support in project decision to risk reduction regarding layers protection as safeguard implementations
or projects modifications. As a matter of fact, the mean focus of Hazop is process deviations nor hazard and
environment aspect and it’s the first limitation. Moreover, even given a high contribution to increase the safety
level plants so many recommendations requires safeguards and it’s can lead Plants to unsafe condition regarding in
some specific events, so many visual alarms and others safeguards are released in the same time that operator have
no condition to pay attention in all of then and it’s may happen an accident. So the recommendation consistence
is necessary to keep safety level and reduce the layers protections that not contribute to risk reduction.
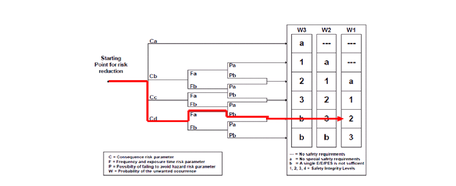
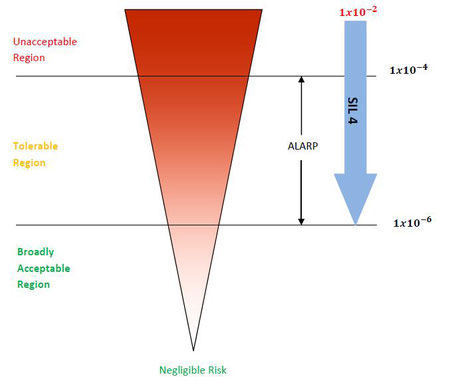
The SIL analysis has the mean objective to check the reliability level of safety functions and if it’s necessary, to
propose configuration improvement to increase safety levels. There are qualitative and quantitative SIL analysis
methodology, The matrix methodology, Risk graph, Assignment base on frequency and Assignment based on
individual and society risk. All of that methodology permit to identify SIL and propose improvements to achieve
SIL target that’s is defined for specific standards or for company standards. Therefore, that’s an important risk
analysis to check HAZOP consistence.
The SIL application will be shown in a refinery study case as a consistence analysis of HAZOP analysis to
check if the recommendation is enough to achieve the SIL required or not and in which cases it’ll be necessary
increase or reduce safety levels.
Key words: HAZOP, SIL analysis, Matrix methodology, Risk Graph, Individual risk
RGBI: Reliability Growth Based Inspection
Abstract
The main objective of this study is to propose a methodology to define the operational availability for a system in different interval of time based on Monte Carlo simulation. In addition, it is
also an objective to identify critical equipment in such interval of time and define when carrying out inspections to detect and prevent failures. Nowadays, many software packages which apply
Monte Carlo simulation based on reliability diagram block do not show the operational availability defined by interval of time. In most of cases, there’s no result that shows how system performs
in specific interval of time. Depending on situation, it’s important to define the operational availability by different interval of time in order to follow up system performance along time. In
order to solve such problem, it is proposed the “partial availability methodology” based on system age. Indeed, such method regards equipment age based in different period of time that will
results in Partial Availability. That means, as instance, in case of two years of simulation there will be the cumulative operational availability and partial operational availability results for
first and second years for example. Therefore, it is also important to define the inspection time in each interval of
time (year) in order to detect possible equipment failure and define preventive maintenance to avoid such failures that will be performed by RGBI method. In order to show such methodologies, it
will be carried out a drill facility case study which is required to define operational availability of the system on the first and second years as well as inspection time.
Keywords
Partial Operational Availability, System Age, Probability Density Function (PDF),Reliability Growth and inspection time.
RAM Analysis applied to Oil and Gas II
ABSTRACT:
In order to predict future failures and define critical equipment it is necessary to take into account the positive or negative maintenance effect on equipment reliability. Therefore, the
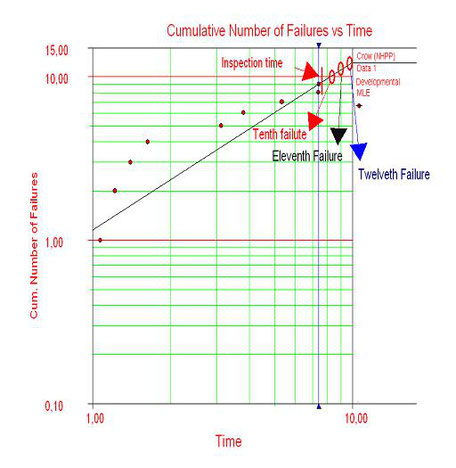
Reliability Growth Analysis (RGA) applied to a repairable system can be performed to predict the cumulative number of failures, considering the degradation effect of repairable equipment.
Despite RGA being the best approach, in some cases it is necessary to consider the system configuration modelling RBD (Reliability Block Diagram) and perform a direct simulation to predict system
operational availability and expected number of future failures. Therefore, the General Renewal Model is required to define the restoration factor of each equipment item in order to take into
account the degradation effect on equipment performance and apply these factors to RBD configuration in order to predict the system operational availability and future expected number of failures
with respect to the degradation effect.
The restoration factor is minted to give values between zero and one. In other words, a restoration level between “as bad as old” and “as good as new”. The RGA model deems the restoration levels as “as bad as old” and “as good as new” and “better than as good as new”.
Therefore, the proposal methodology predicts the restoration factor from the RGA model, based on a likelihood method. In addition, the expected number of future failures is determined by
comparing the prediction results from RGA model (Crown AMSAA Model) and direct simulation (MC) which considers the restoration factor.
The main objective of this paper is to present these particular reliability engineering methods and demonstrate the application on an asset case study in decommissioning phase. The simulation for
cumulative time as well as a specific period of four months was carried out in order to predict the effect of critical failures on system operational availability during a specific range of time.
key words: RAM analysis, RGA, Lifetime Data Analysis,General Renew Model
RAM Analysis applied to oil and gas I
Abstract:The main objective of the RAM analysis (Reliability, Availability and Maintainability) is assessing equipment or system performance throughout critical equipment
improvement in order to achieve an operational availability and production efficiency target. To carry out RAM analysis, it is necessary to define the equipment failure modes which have the
highest impact on system availability. The analysis is carried out using historical failure data and repair time and simulation using a reliability diagram model model. Despite widespread
applicability of this methodology for large, complex systems it is vitally important that logistics issues must to be considered. There are two different approaches, the first one focuses on
reliability issues and the second one on logistic. At this time in Brazil there is no methodology which considers these two issues, logistic and reliability in only one Methodology, in order to
assess huge logistic system regarding reliability issues of subsystems and equipment into logistic systems. In fact complex logistic systems analysis does not take into account reliability issues
and the other way rounds.
The RAM + L analysis methodology takes into account logistic and reliability issues in order to have a more representative result to support improved decisions. The case study consists of a
complex system comprising refineries plants (Vacuum and Atmospheric Distillation Plant, Thermal Cracking Plant, Acid Water Plant, Cracking Catalytic Plant, Reforming Catalytic Plant, Fractioning
Plant, DEA, Nafta and Diesel Hydrodesulphurization Plant) and Tanks will be carried out to assess advantages, drawbacks and to compare RAM analysis with the results obtained using the RAM + L
analysis.
Keywords: RAM Analysis, RAM + L Analysis, logistic, availability, MAROS, TARO.
Human Reliability Analysis
Human factors always affect maintenance performance, and in some cases, it’s critical to systems availability and reliability. Despite such importance, in so many cases, there’s no human reliability method applied to analyze maintenance tasks in order to understand better human factors influence in maintenance performance. There are several human analysis methodologies and regarding human factors, SLIM (Successes Likelihood Methods), SPAR-H (Standardized Plant Analysis Risk-Human Reliability Analysis Method) and Bayesian Net take into account such factors and may be a good approach to minimize human error. In order to propose a human reliability methodology to analyze maintenance tasks taking into account human factors, a case study about turbine star up tasks will be carried out. Therefore, different human reliability methods will be performed based on specialist opinion. Finally, the human error probability as well as drawbacks and advantages from different methods will be discussed to get a final conclusion.
Keywords: Human Reliability Analysis; Human Performance Factor; Human Error Probability
Risk Assessment
ABSTRACT: Nowadays one of the most important decisions in safety issues in Brazilian Oil and Gas industry is that it’s necessary to shut down plant because one specific failure or required maintenance in protection system makes influence on risk level. Most of time, experienced operators make decisions based on their background despite carrying out a risk analysis to support their decision. Therefore in so many cases, refinery plants work on catastrophic risk level due to subjective decisions. In order to improve the operator decision, a specific methodology was established to apply risk assessment using PRA (Preliminary Risk Analysis), LOPA (Layer of Protection Analysis) and FTA (Fault Tree Analysis) in order to check risk level or layer of protection availability. By this way, as the first step, the Preliminary Risk Analysis will be carried out in order to qualify risk and mainly define consequences severity. The second step will carry out the LOPA in order to find out the failure probability of all layers of protection and without one of those layers of protection which requires maintenance or even failure. In addition, when is necessary to check that contingency systems availability FTA will be carried out? In the first case, it is possible to substitute the layer of protection for another in order to keep risk on acceptable level. In the second case, it is necessary to check if contingency system is available and assess if consequence gets worse or keeps on the same level. In both cases, the final risk will be assessed and compared with the pre-vious one defined on PRA. In case of risk, it is unacceptable that the final decision will shut down plant. The refinery study case will be shown as an instance of such methodology.
Keywords: Preliminary Risk Analysis; Fault Tree Analysis; Layer of Protection
RAM Analysis for RAILWAY INDUSTRY I
ABSTRACT: Nowadays the RAMS process is very well described in EN50126 by “V Diagram” regarding which activities is necessary in railways life cycle phases. Nevertheless, it is
not clear which are the specific reliability engineer and risk analysis methods must be applied in order to achieve high performance a long railways life cycle. The methodology described on
EN50126 does not consider explicitly for example reliability engineer methods like accelerated test, growth analysis, Life cycle analysis, RAM analysis by Monte Carlo Simulation a long
enterprises life cycle.
In many cases, the train industry carry on RAMS and life Cycle Cost to manage their asset but do not optimize the reliability engineer methods to get better results. The equipment life cycle
analysis, RAM analysis, Accelerated test, Reliability Growth Analysis, DFMEA, FMECA, RCM and Human reliability analyze are not applied intensively and correctly a long train life cycles to obtain
better results. The main objective of this paper is to show how to integrate different equipment and system from differen suppliers in one unique integrated model to enable to compare different
trains configuration.
Key Words: FMEA, RCM, RAM, LDA, FTA
RAM Analysis for Railway Industry II
RAMS analysis has main objective to define system availability, reliability and maintainability regarding critical equipment failures and safety issues like incidents and accidents which impact
on system availability and employees health. On most of industries, the reliability diagram block is applied to model the complex systems. Regarding safety, in many cases, incidents are results
of combined events which are better modeled by Fault tree analyses. Nowadays the RAMS process phases is very well described in EN50126 by “V Diagram” regarding which activities is necessary in
railways life cycle phases. Nevertheless, it is not clear which are the specific reliability engineer methods which must be applied in order to achieve high performance a long railways life
cycle. The methodology described on EN50126 does not consider such application and integration of RBD and FTA as well as Monte Carlo Simulation. In addition, it is no mentioned others reliability
engineer tools like accelerated test, growth analysis, Life cycle analysis a long enterprises life cycle.
Furthermore, regarding Safety, the Preliminary Hazard Analysis has been the most qualitative risk analysis applied to define hazard events but in most of cases such events are not quantified by
FTA and when such events are modeled do not take into account the incidents effect on system availability. On Transportation Industry, the RAMS process analysis carries out RAM and safety access
separately. This paper propose to integrate incident and equipment failures which affect System availability by RBD and FTA model and Monte Carlo Simulation in order to find out all events that
causing System unavailability as well as define all incidents events which cause employees health damage.
Key Words: Critical equipment, operational availability, reliability, number of failures